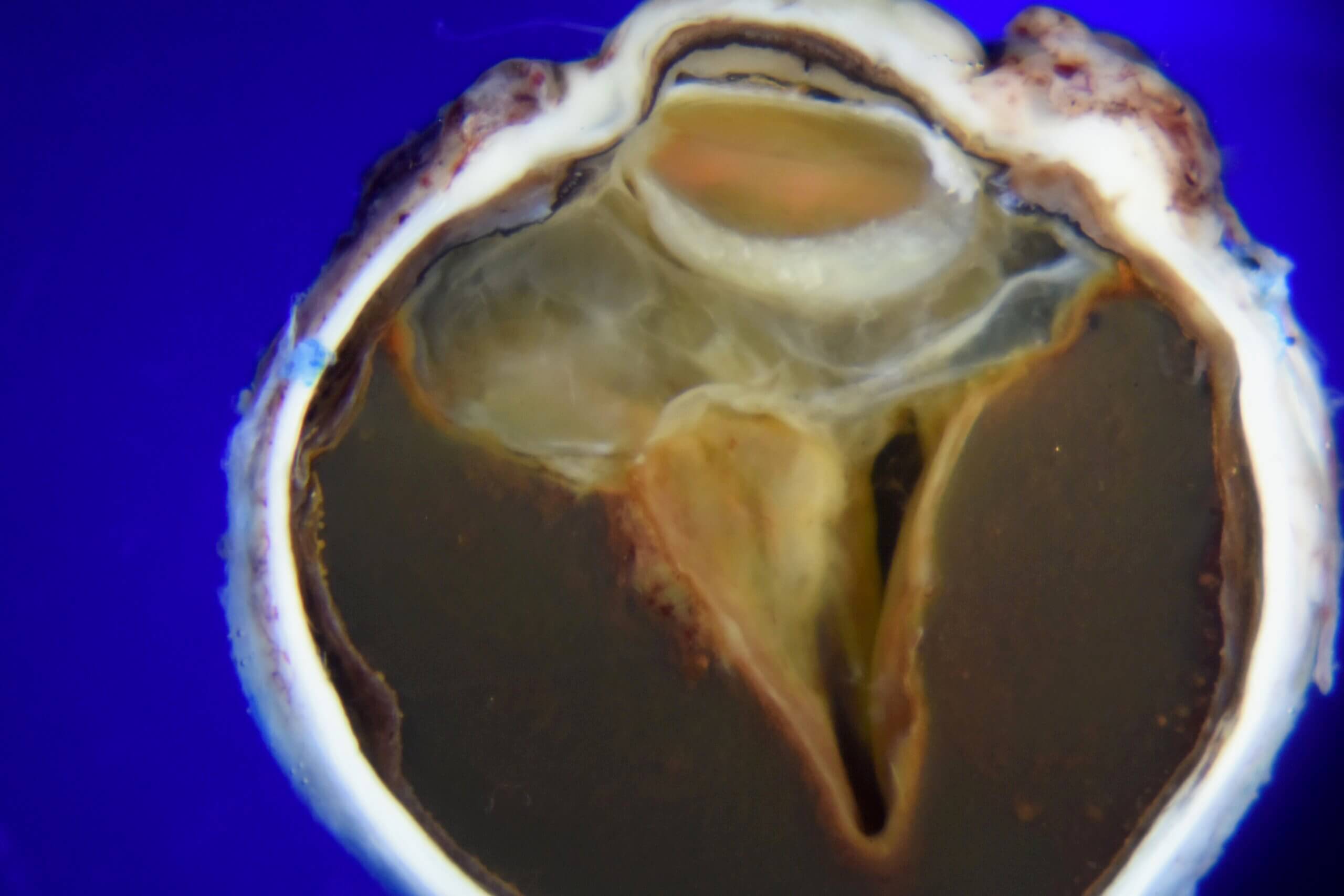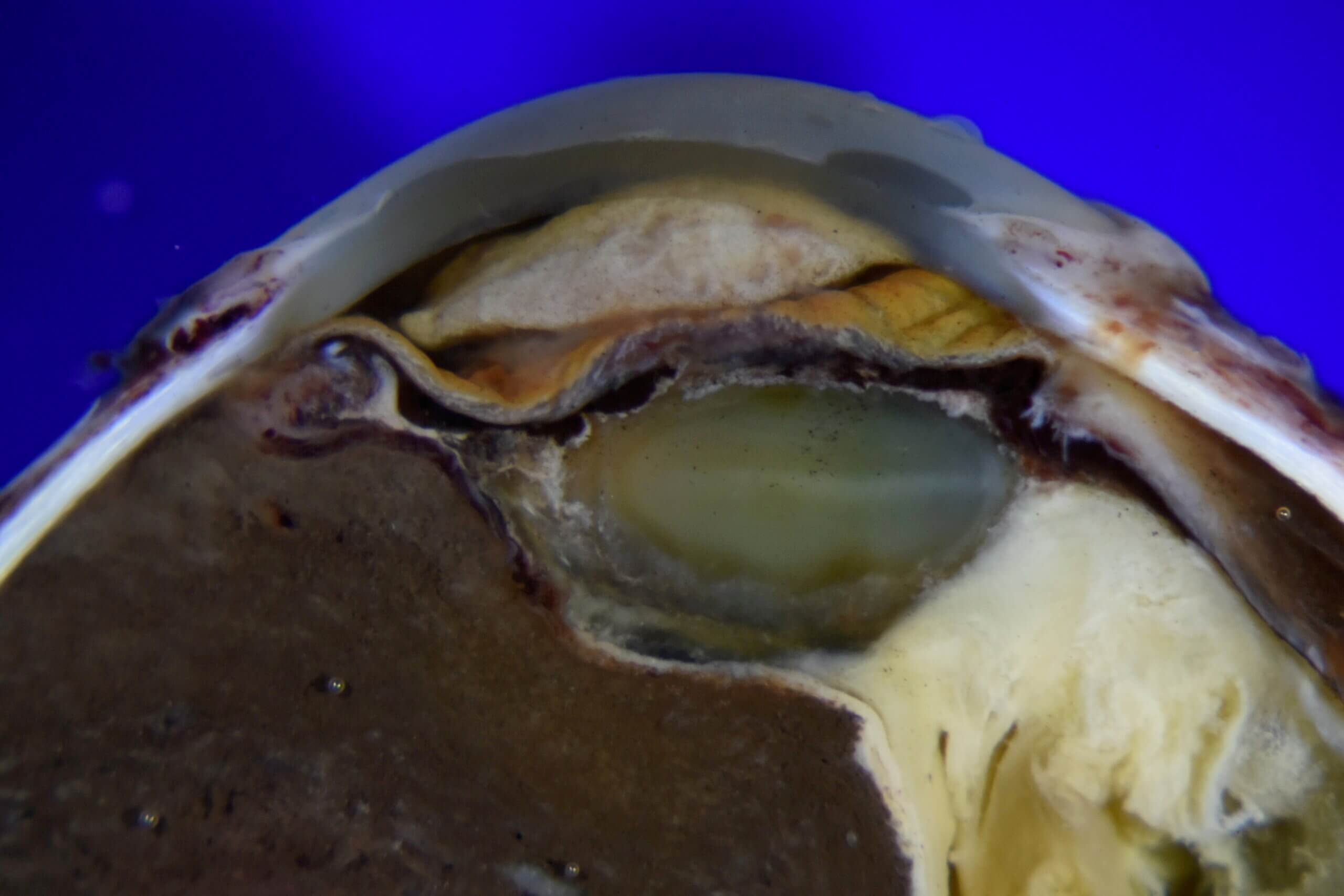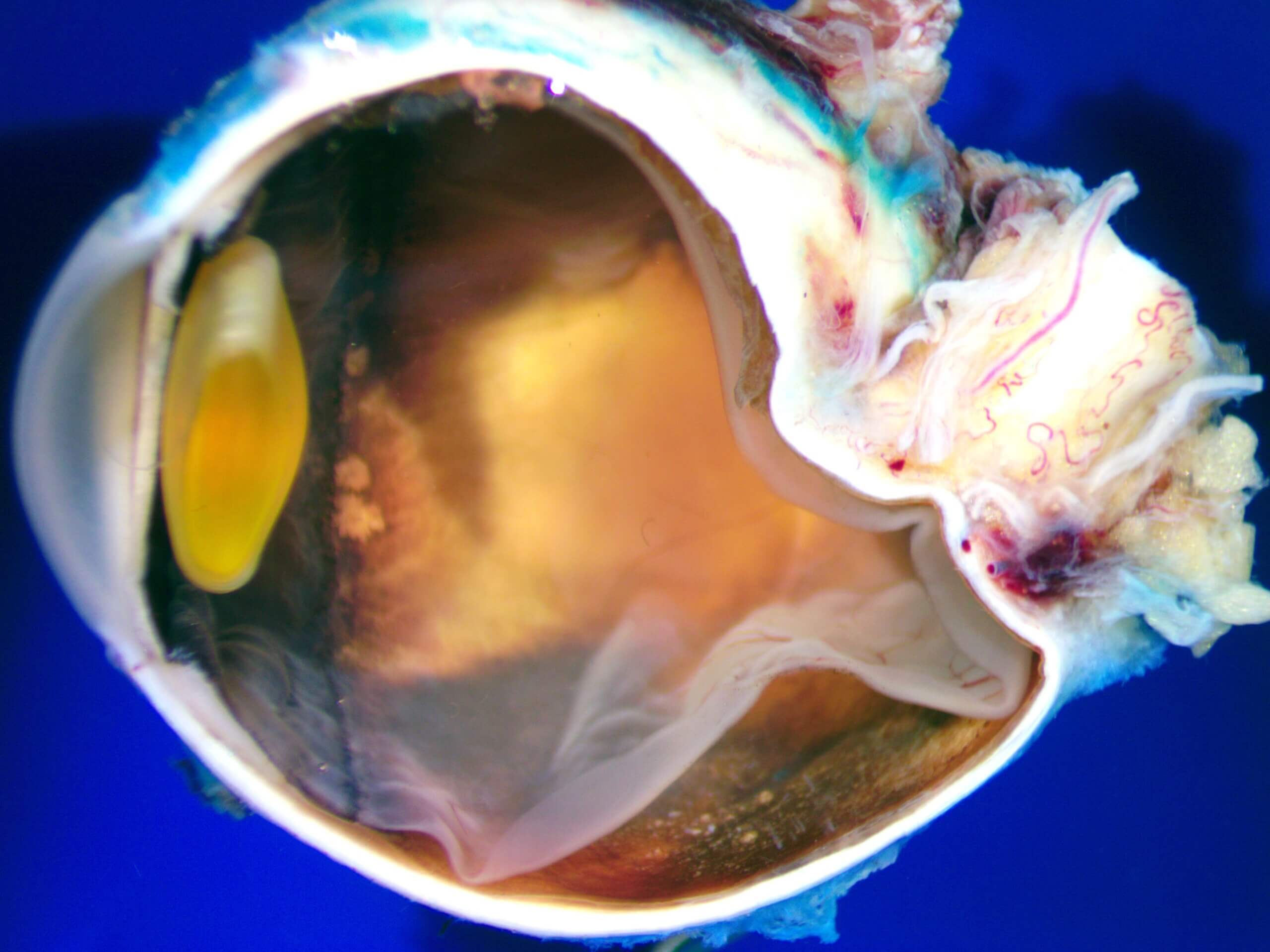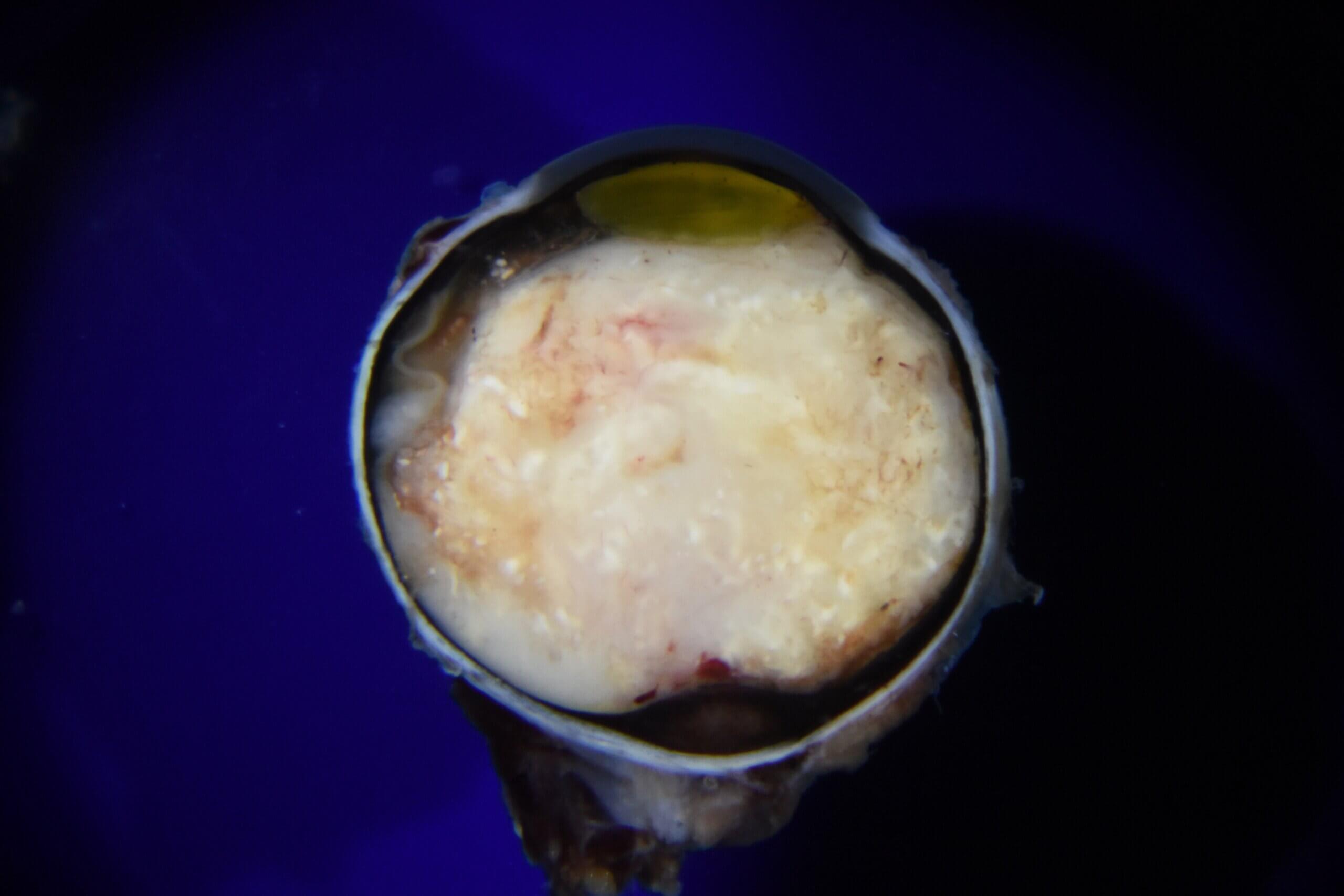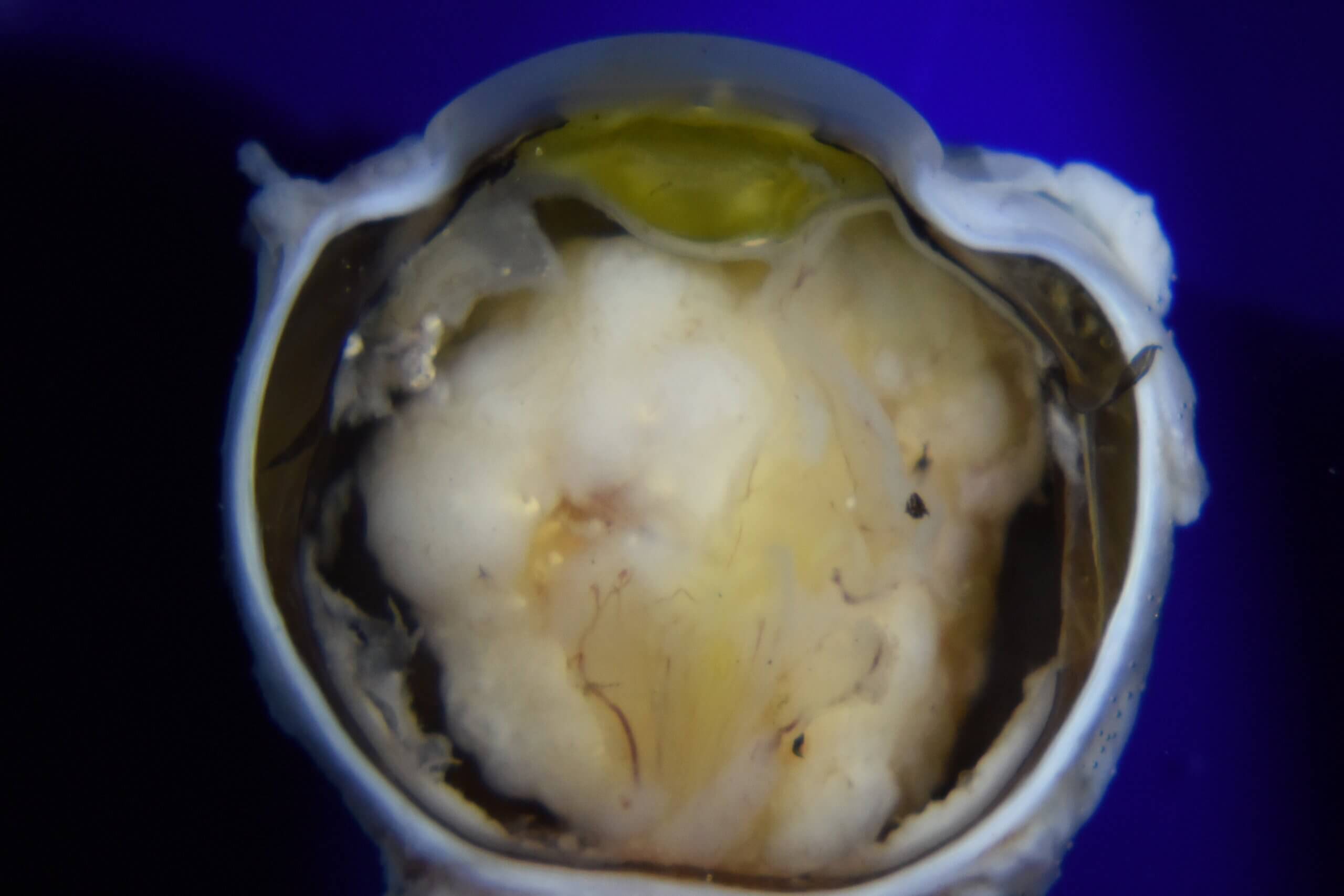









PATHOLOGY-RELATED VIDEO ARCHIVES
Anterior segment pathology refers to diseases affecting the front part of the eye, including the cornea, iris, ciliary body, and lens. Common conditions include uveitis, cataracts, corneal abrasions, and glaucoma. Anterior segment pathology can also involve structural abnormalities like anterior segment dysgenesis.
Eye pathology involves examining tissue samples (surgical, biopsy, or autopsy) under a microscope to diagnose diseases, determine their cause, and guide treatment and research
Pathology helps neuro-ophthalmology by providing critical tissue-based diagnoses for eye and neurological diseases, particularly those affecting the visual pathways.
Ophthalmic pathology plays a crucial role in ocular oncology by providing the precise diagnosis of ocular tumors, which is essential for determining the most appropriate treatment plan and prognosis. Ophthalmic pathologists examine both gross and microscopic samples of eye and orbital tissues, including surgically removed tumors, to identify the specific type of cancer, its stage, and any other relevant features
Pathological examination of surgical specimens and post-operative biopsies can aid in monitoring for recurrence or progression of disease, guiding ongoing management and follow-up strategies. Orbital biopsies are particularly helpful when a clinical or radiological diagnosis is not readily established, allowing for definitive identification of the underlying pathology.
Ocular pathology can be used to confirm or rule out specific genetic diagnoses, especially in cases where clinical features are not clear-cut. For example, immunohistochemistry and molecular testing can help identify genetic mutations or gene fusions associated with certain eye cancers or other inherited eye diseases.
Ophthalmic pathology can pinpoint the cause of various eye conditions in children, including genetic disorders, infections, and tumors. This is crucial for early intervention and preventing lifelong vision impairment.
Retinal pathology refers to any disease or abnormality of the retina, the light-sensitive tissue lining the back of the eye. These conditions can range from congenital anomalies to degenerative diseases, and can impact vision in various ways. Common examples include retinal tears, retinal detachments, diabetic retinopathy, and macular degeneration.

Dr. Patricia Perez Cuesta
Editor


RESIDENT CASE

Presentation
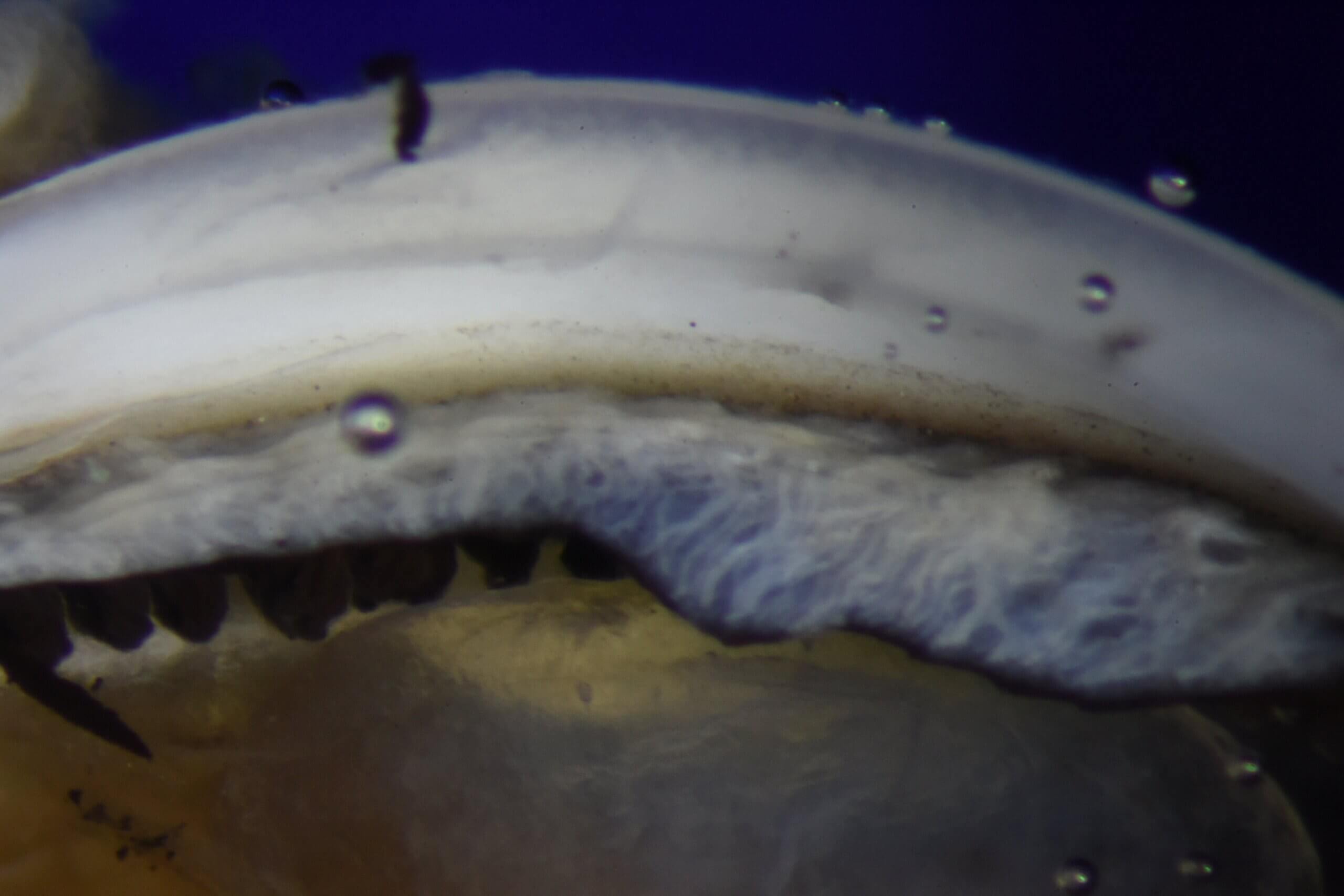
A 54-year-old male line worker presented to a community hospital after an arc flash from a malfunctioning powerline transformer (estimated 7,200-volt flash). He was a few feet from the transformer and wore recommended personal protective equipment, including industrial UV-tinted protective eyewear.
On ophthalmic consultation, he reported several minutes of severe blurring immediately after the flash, followed by persistent mild blurriness and burning eye pain OU. He reported a sandpaper sensation with eyelid closure that improved with proparacaine. He also had mild photophobia but no flashes, floaters or other vision symptoms.
Photographic images by Wills Eye residents and fellows.
(Scroll to view images from prior months
This month's image presented by:

Joseph DeSimone, MD

Nelle Shields, MD

Minjia Tang, MD

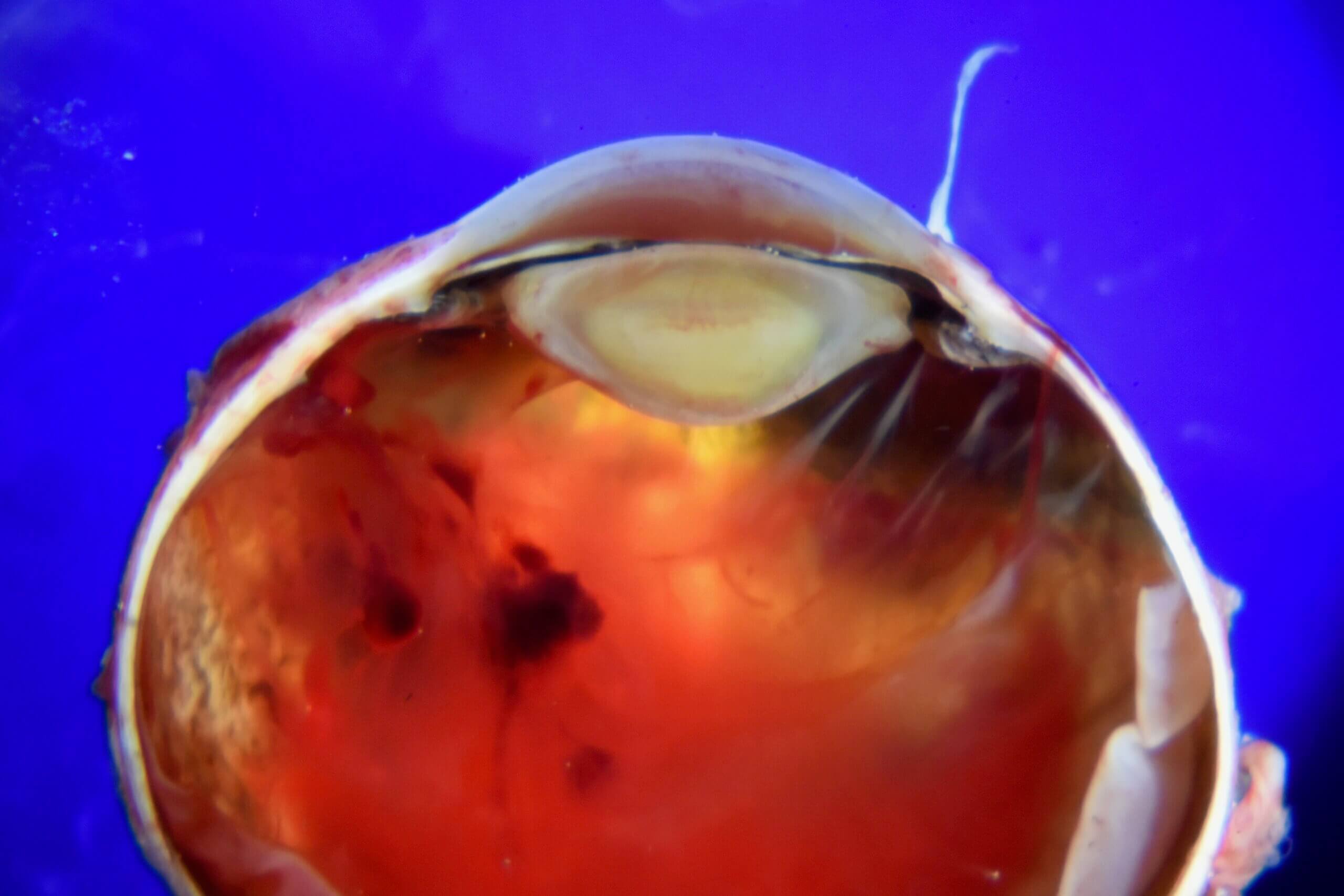
HSV dermatitis with associated keratitis
Representative histology shows epithelial cells with HSV cytopathic changes, including multinucleation, nuclear molding, and Cowdry type B inclusions with chromatin margination.
This month's image presented by:

Martin Calotti, MD.
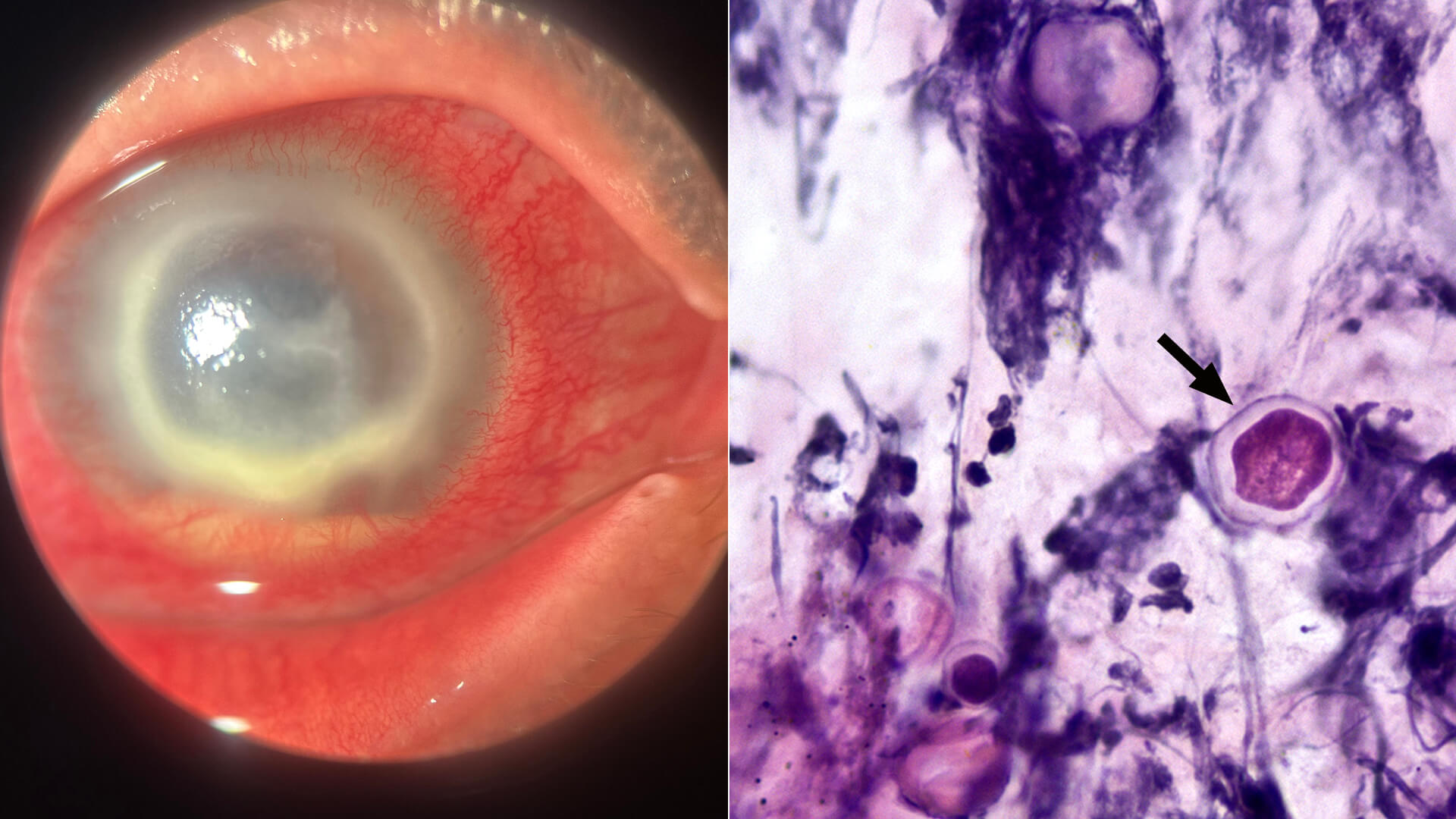
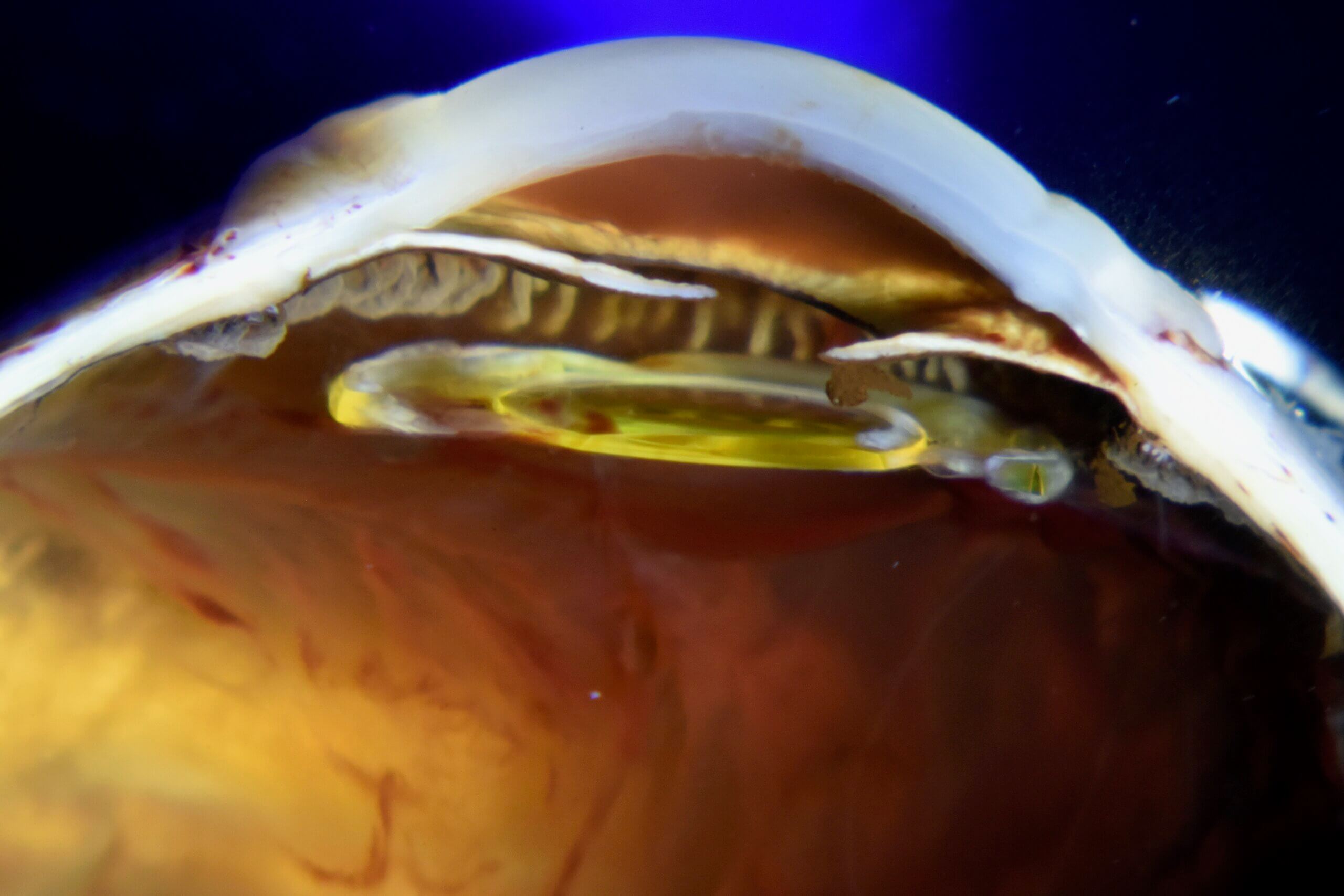
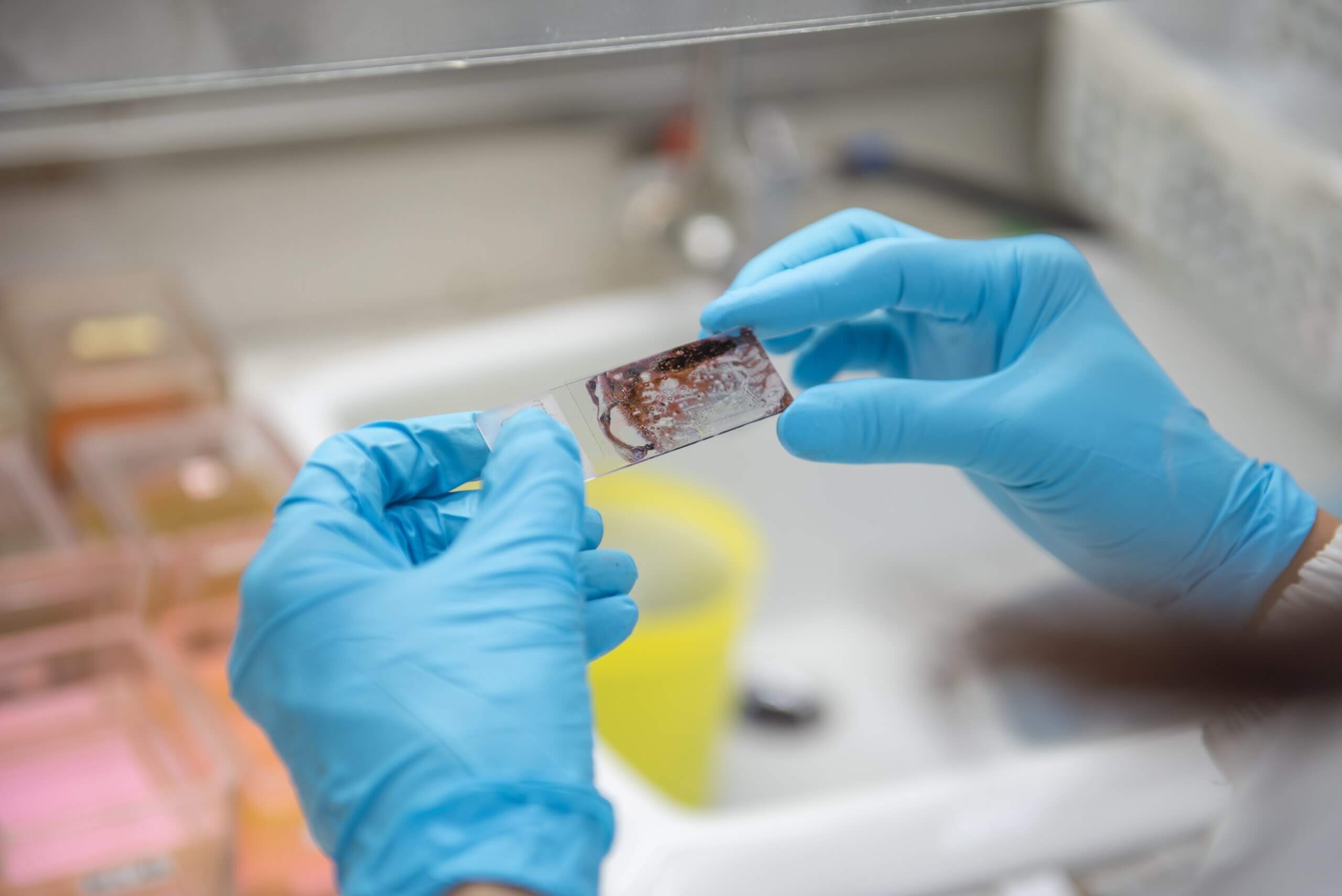
Acanthamoeba keratitis presenting as a ring ulcer
Corneal scrape biopsy shows intact (arrow) and degenerated Acanthamoeba.
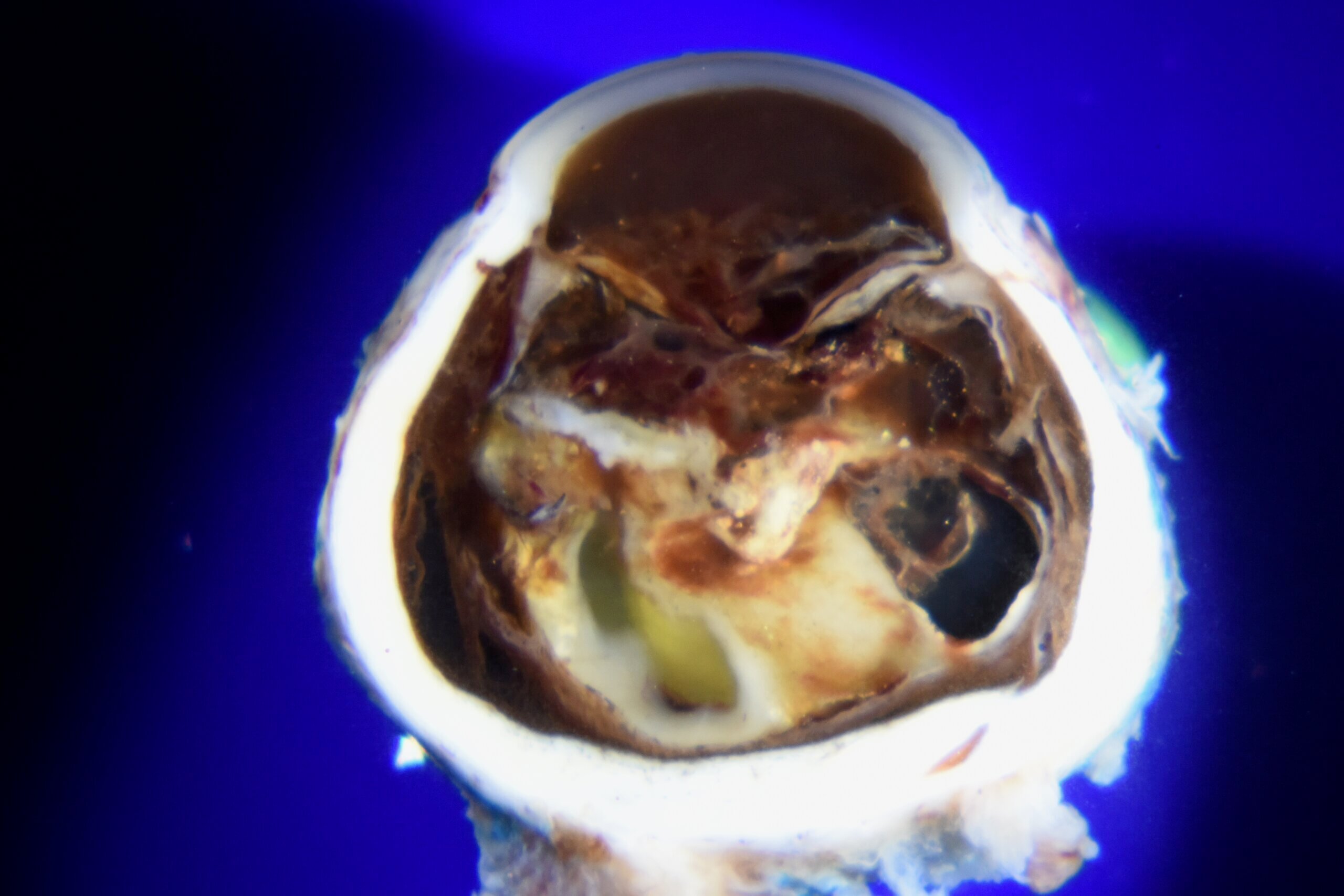
This month's image presented by:

Eric Kim, MD
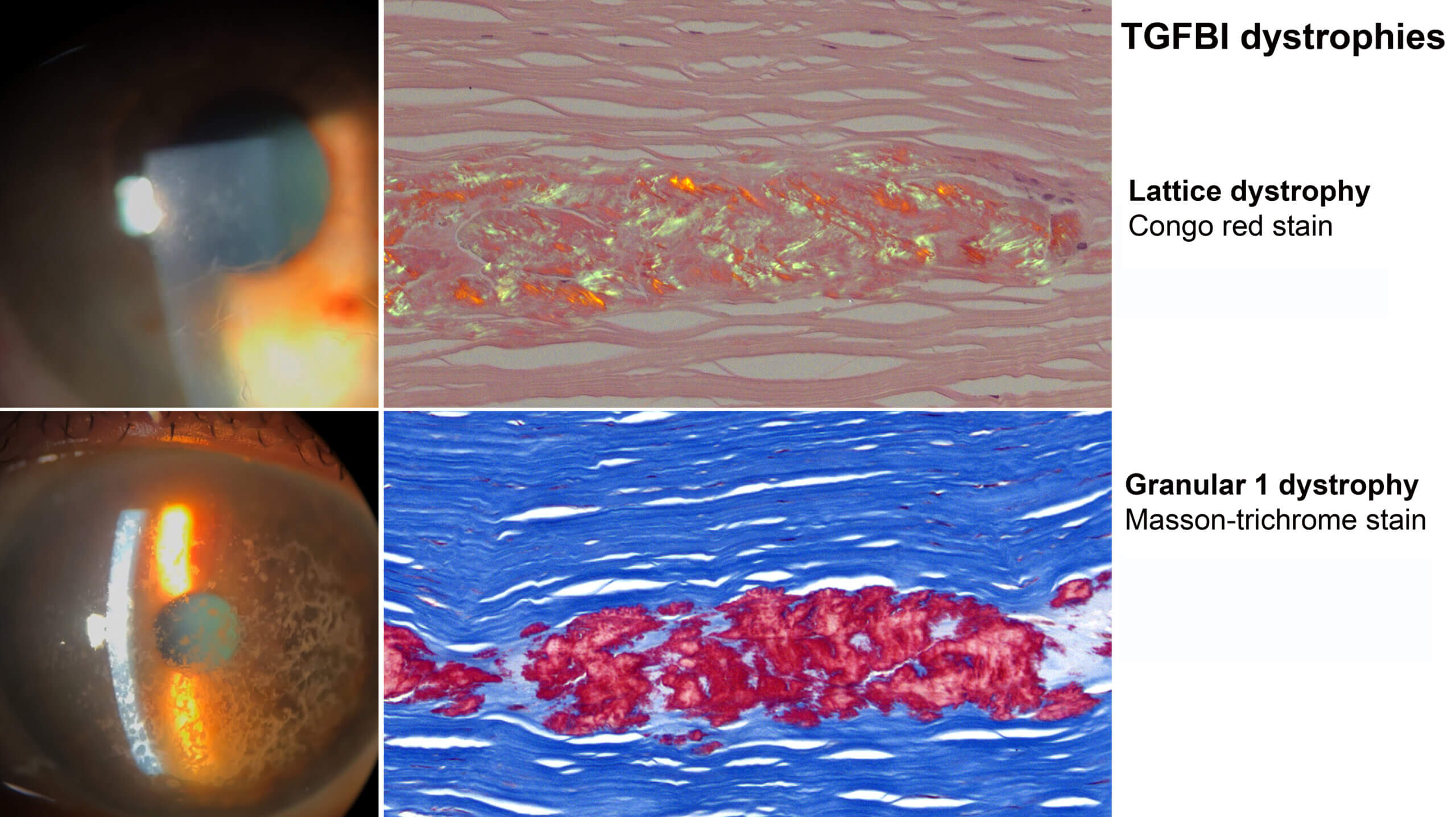



Corneal Dystrophies and Simulating Lesions

Explore our growing collection of educational videos created by pathology fellows, offering step-by-step guidance on proper handling, processing, and evaluation of ophthalmic specimens.
This resource is designed to support both training and practice in ophthalmic pathology.
Check back soon for the full video series.
List of providers who offer expert consultations in eye pathology.
Join the leading experts dedicated to advancing ocular pathology and ocular oncology.

The International Society of Ocular Oncology (ISOO) is a non-profit corporation with the specific and primary purpose to advance and promote the practice of ocular oncology. For information, click here.

The mission of the Ocular Oncology Service at Wills Eye Hospital is to provide the most skilled care for patients with ocular tumors and cancers in a compassionate way with the ultimate goal to save life and sight. For information, click here.

The American Association of Ophthalmic Oncologists and Pathologists (AAOOP) offers membership opportunities for trainees, ophthalmologists, and pathologists. For information, click here.
Philadelphia, PA 19107

For additional information or comments, please contact:
Tatyana Milman, MD at:
tmilman@willseye.org